As the world transitions towards sustainable energy sources, biodiesel has emerged as a promising alternative to conventional fossil fuels. In this article, we will explore what it is, its benefits, production process, and its impact on the environment.
What is Biodiesel?
It is a renewable and environmentally friendly fuel made from organic sources, primarily vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils. You can use it in any diesel engine without modification, making it an excellent alternative to traditional diesel.

Benefits of Biodiesel
Renewable Energy Source:
Unlike traditional diesel, which is a finite resource, it can be produced indefinitely from organic sources
Lower Carbon Emissions
It produces significantly fewer carbon emissions compared to fossil fuels, making it a more environmentally friendly alternative
Domestic Production
It can be produced locally, reducing dependence on foreign oil and improving national security
Engine Durability
It has excellent lubricating properties, reducing engine wear and extending engine life
Types of Biodiesel feedstocks
- Plant-Based Oils: The most common sources are soybean, rapeseed (canola), and palm oil. These are rich in triglycerides, making them ideal for biodiesel production
- Animal Fats: Producers use tallow, lard, and other animal fats to create biodiesel, adding an extra revenue source for the agricultural sector.
- Waste Oils: Restaurants and food processing plants repurpose recycled cooking oil into biodiesel, promoting waste reduction.
- Algae: Research is ongoing into algae as a sustainable and high-yield source of biodiesel due to its fast growth and high oil content.
Production Process
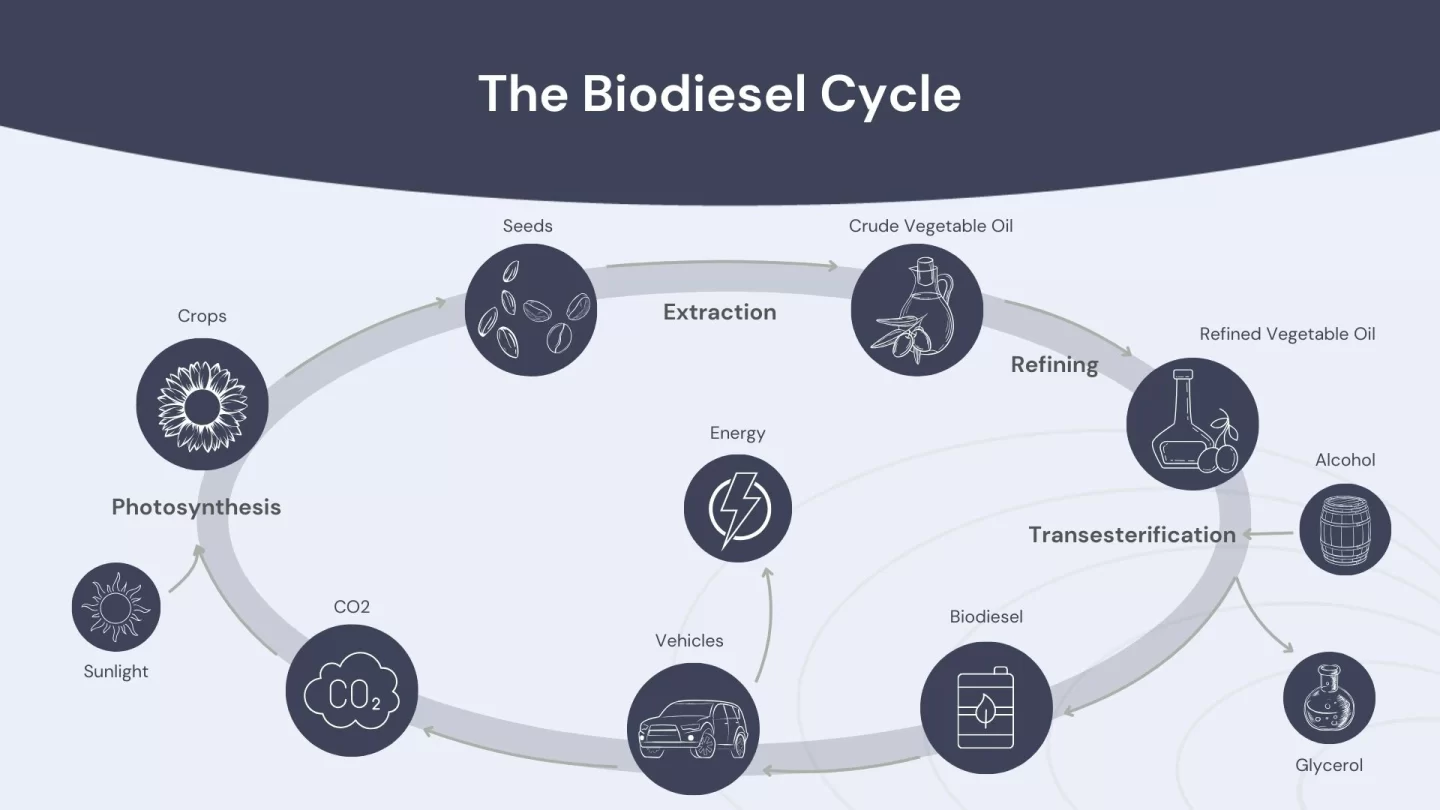
The biodiesel cycle begins when crops like sunflowers or soybeans absorb CO2 and sunlight during photosynthesis to produce seeds. These seeds are processed to extract crude vegetable oil, which is then refined for fuel use. In the transesterification process, producers mix the refined oil with alcohol (like methanol) and a catalyst, breaking down the oil molecules and replacing them with alcohol molecules to create biodiesel. The process also yields glycerol, which is used in the food and cosmetics industries. This renewable biodiesel powers vehicles, helping cut carbon emissions and reduce the use of fossil fuels.
Impact on the Environment
Biodiesel has a significantly lower environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. It produces 60-90% fewer greenhouse gas emissions and reduces the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. Also, it reduces the reliance on foreign oil, which helps minimize the need for importing fuel from politically unstable regions. Additionally, transporting oil carries environmental risks, such as potential ocean spills.
Conclusion
Biodiesel is a promising alternative to traditional diesel, offering numerous benefits, including renewable energy, lower carbon emissions, and engine durability. Additionally, the production process is relatively simple and scalable, suitable for both small and large producers based on their requirements. As the world continues to move towards sustainable energy sources, it will undoubtedly play a critical role in reducing carbon emissions and improving environmental sustainability.
Frequently asked questions
What is biodiesel, and what is it made of?
Biodiesel comes from renewable, organic sources such as vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils. It serves as an effective substitute for traditional diesel, as it can be used in any diesel engine without requiring modifications.
What are the benefits of using biodiesel over traditional diesel?
Biodiesel has several benefits over traditional diesel. These include being a renewable energy source, producing significantly fewer carbon emissions, reducing dependence on foreign oil, and extending engine life due to its excellent lubricating properties.
What is the production process of biodiesel, and how is it environmentally friendly?
The transesterification process produces biodiesel by combining vegetable oil or animal fat with an alcohol, such as methanol, and a catalyst, typically sodium hydroxide. This method creates biodiesel and separates glycerin, which is sold as a byproduct. Biodiesel has a significantly lower environmental impact than fossil fuels. It produces 60-90% fewer greenhouse gas emissions and reduces the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.






