What is Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a vital technology that plays a significant role in mitigating the impacts of climate change. As the world continues to rely on fossil fuels to meet its energy needs, the emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases continue to rise, leading to global warming and other environmental concerns.

What is the process of CSS?
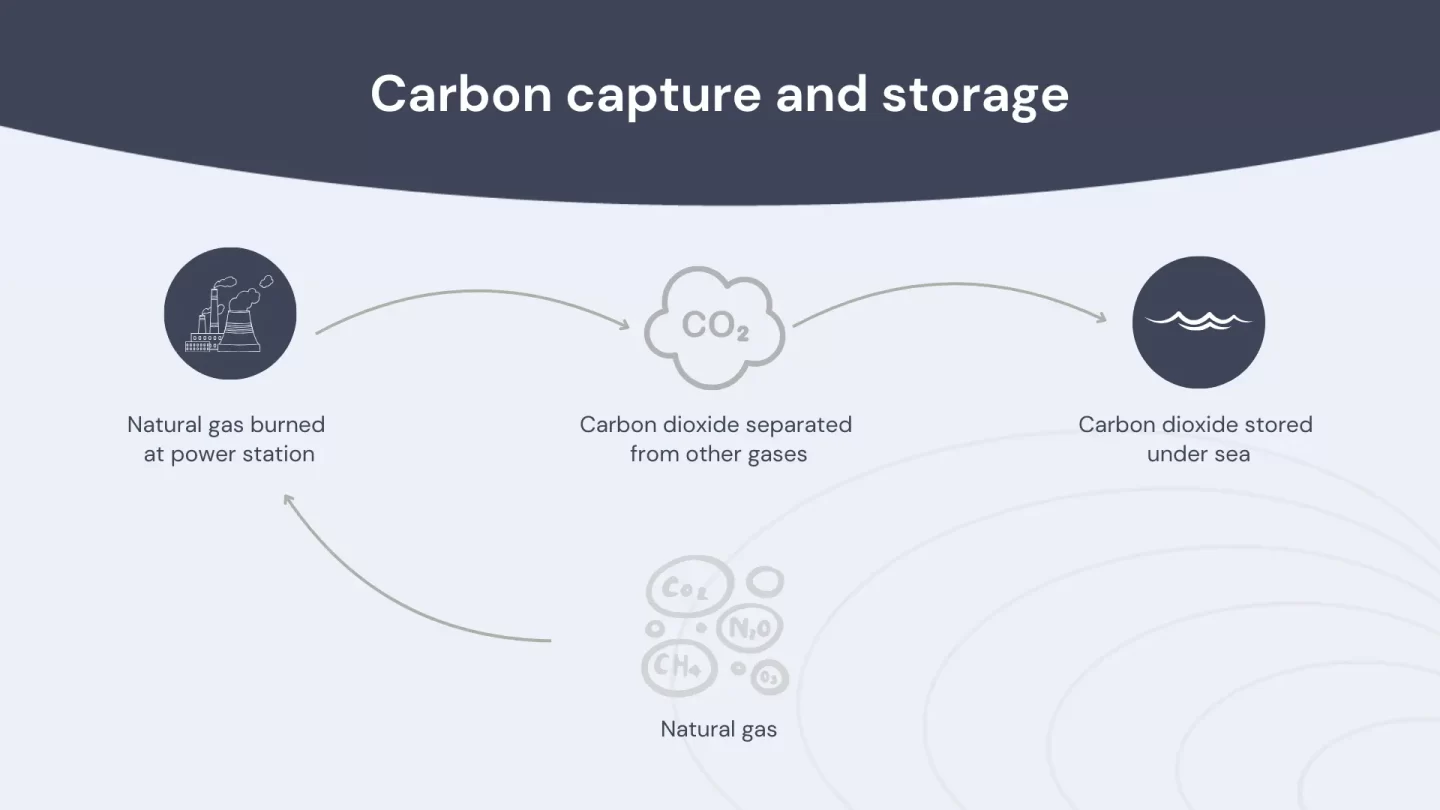
CCS captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from power plants and other industrial sources before releasing them into the atmosphere. Operators then transport and store the captured CO2 underground in geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers. This process prevents the carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere, thereby reducing the impact of greenhouse gases on climate change.
The technology behind carbon capture and storage is relatively simple. The CO2 is first captured through a process known as post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, or oxyfuel combustion. Post-combustion capture involves capturing CO2 from the flue gases emitted by fossil fuel power plants. Pre-combustion capture captures CO2 before burning the fuel.Oxyfuel combustion burns the fuel in pure oxygen to produce a pure stream of CO2.
Once the CO2 is captured, it is compressed into a dense liquid form and transported via pipelines or ships to underground storage sites. They carefully choose these storage sites to ensure that the CO2 remains trapped underground for thousands of years, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Carbon Capture and Storage
The benefits of CCS
1. It reduces the amount of CO2 emissions that enter the atmosphere, which is crucial in mitigating the impact of climate change.
2. Operators can use it with existing fossil fuel power plants, making it a cost-effective option for reducing emissions.
3. It has the potential to create jobs and stimulate economic growth, particularly in regions with abundant fossil fuel resources.
The concerns associated with CCS
Critics argue that it is expensive and that the technology is still in its infancy.
Others are concerned about the safety of storing large quantities of CO2 underground and the potential for leaks.
However, many experts believe that continued research and development can address these concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon capture and storage is an essential technology that has the potential to play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of climate change. By capturing CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants and storing them underground, CCS can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help to create a more sustainable energy future. As we continue to search for alternative sources of energy, carbon capture and storage is likely to become an increasingly important part of the energy mix.
Frequently asked questions
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) captures carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from power plants and other industrial sources before releasing them into the atmosphere. Operators then transport the captured CO2 and store it underground in geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers. This process prevents the carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere, thereby reducing the impact of greenhouse gases on climate change.
The benefits of CCS include reducing the amount of CO2 emissions that enter the atmosphere, using existing fossil fuel power plants, and creating jobs and stimulating economic growth. However, concerns associated with CCS include cost, the technology being still in its infancy, the safety of storing large quantities of CO2 underground, and the potential for leaks.
Carbon capture and storage is an essential technology that has the potential to play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of climate change. By capturing CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants and storing them underground, CCS can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help to create a more sustainable energy future. As we continue to search for alternative sources of energy, carbon capture and storage is likely to become an increasingly important part of the energy mix.






