What is a condenser?
A condenser converts steam back into water. In power plants, condensers play a critical role in the steam power cycle by recovering the heat energy from the steam and increasing the overall efficiency of the power generation process.

How does a condenser produce energy?
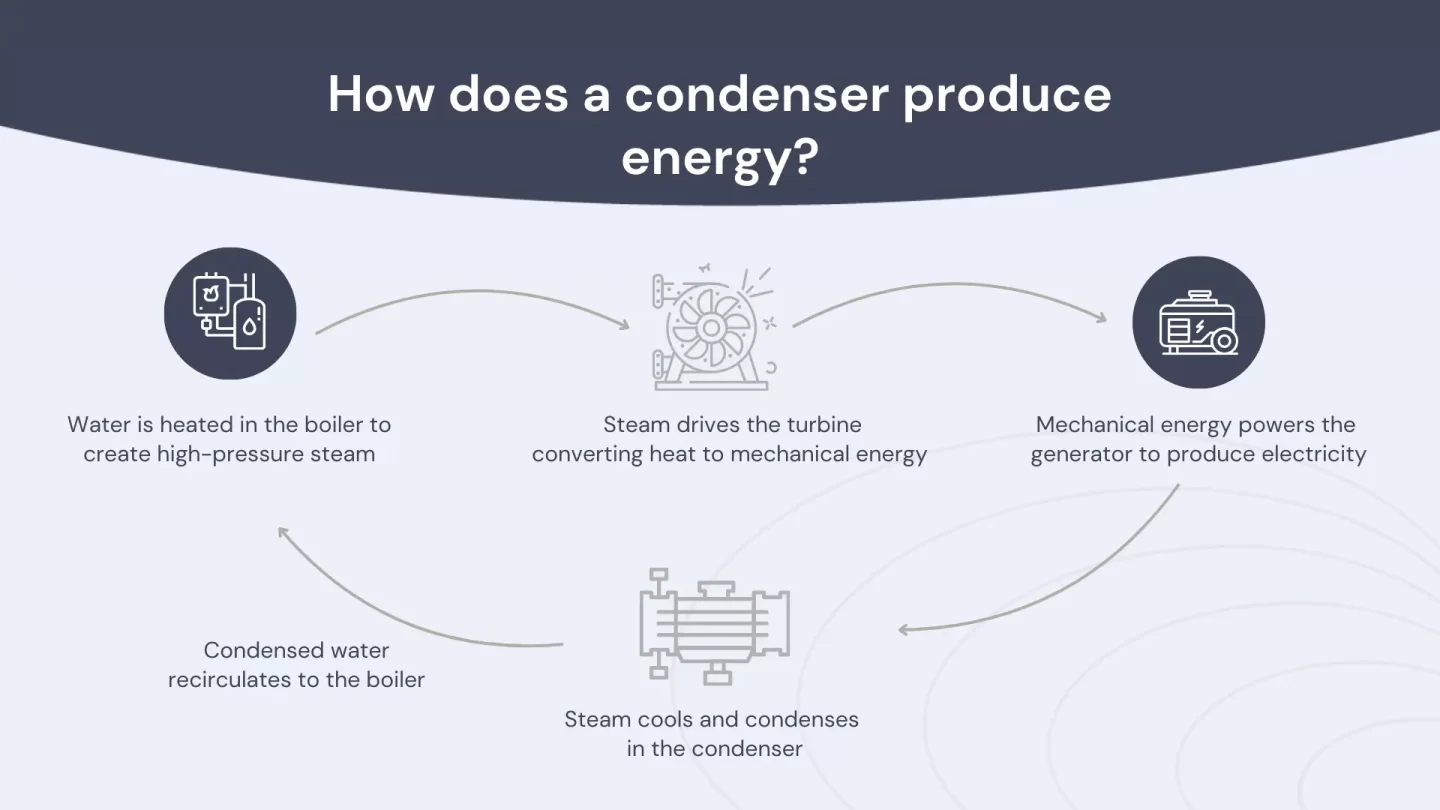
The process of generating electricity in a power plant typically involves the use of a steam turbine. Boiling water in a boiler creates steam, which produces high-pressure steam. This steam then passes through a turbine, converting the heat energy into mechanical energy that drives a generator to produce electricity.
Once the steam has passed through the turbine, it is directed into a condenser. The condenser is typically a large heat exchanger that uses cool water to condense the steam back into water. As the steam condenses, it releases its latent heat energy, which the cooling water then absorbs. The system recirculates the cooled water back to the boiler, where it is heated and turned back into steam.
By recovering the heat energy from the steam through the use of a condenser, power plants can significantly increase their overall efficiency. This is because the heat energy that would otherwise be lost to the atmosphere is instead recycled back into the power generation process.
Types of condensers
Power plants use several different types of condensers, including surface condensers, jet condensers, and direct contact condensers. Each type of condenser has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific needs of the power plant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a condenser can convert steam back into water. In power plants, condensers play a critical role in the steam power cycle by recovering the heat energy from the steam and increasing the overall efficiency of the power generation process. Power plants use several different types of condensers, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
Frequently asked questions
The use of a condenser in a power plant can significantly increase the overall efficiency of the power generation process. By recovering the heat energy from the steam, power plants recycle it back into the process, reducing the amount of energy lost to the atmosphere. This can lead to lower operating costs, improved environmental sustainability, and increased profitability for power plant operators.
The type of condenser used in a power plant depends on a variety of factors, including the size and capacity of the power plant, the specific needs of the power generation process, and the availability of cooling water. Larger power plants typically use surface condensers, while smaller facilities or specific applications may find direct contact and jet condensers more suitable.
Like all mechanical components, condensers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Common issues that can affect condenser performance include scaling, fouling, and leaks. Regular cleaning and inspection can help to prevent these issues and extend the lifespan of the condenser, reducing maintenance costs and downtime for power plant operators.






