Welcome to our comprehensive guide on decentralized energy in the energy industry. In this guide, we will delve into the concept of decentralizing energy, its role in promoting sustainability and resilience, and its various applications across different sectors. Join us as we explore its benefits and potential.
Understanding Decentralized Energy
Decentralized energy refers to energy production and distribution systems that are localized and closer to the point of consumption. It involves generating energy from diverse sources, such as renewable energy technologies, combined heat and power (CHP) plants, and microgrids. This decentralized approach offers numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, reliability, and environmental impact.
Benefits of Decentralized Energy
The decentralization of energy systems provide several benefits:
Sustainability: By utilizing renewable energy sources and promoting energy efficiency, decentralized energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. It supports the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Resilience: Decentralization of energy enhances the resilience of energy systems, particularly in the face of natural disasters, grid failures, or other disruptions. Localized generation and distribution enable communities to maintain access to essential services during emergencies.
Local Empowerment: By decentralizing energy, local communities are empowered by enabling them to actively participate in energy production and decision-making processes. It fosters energy independence, economic opportunities, and community engagement.
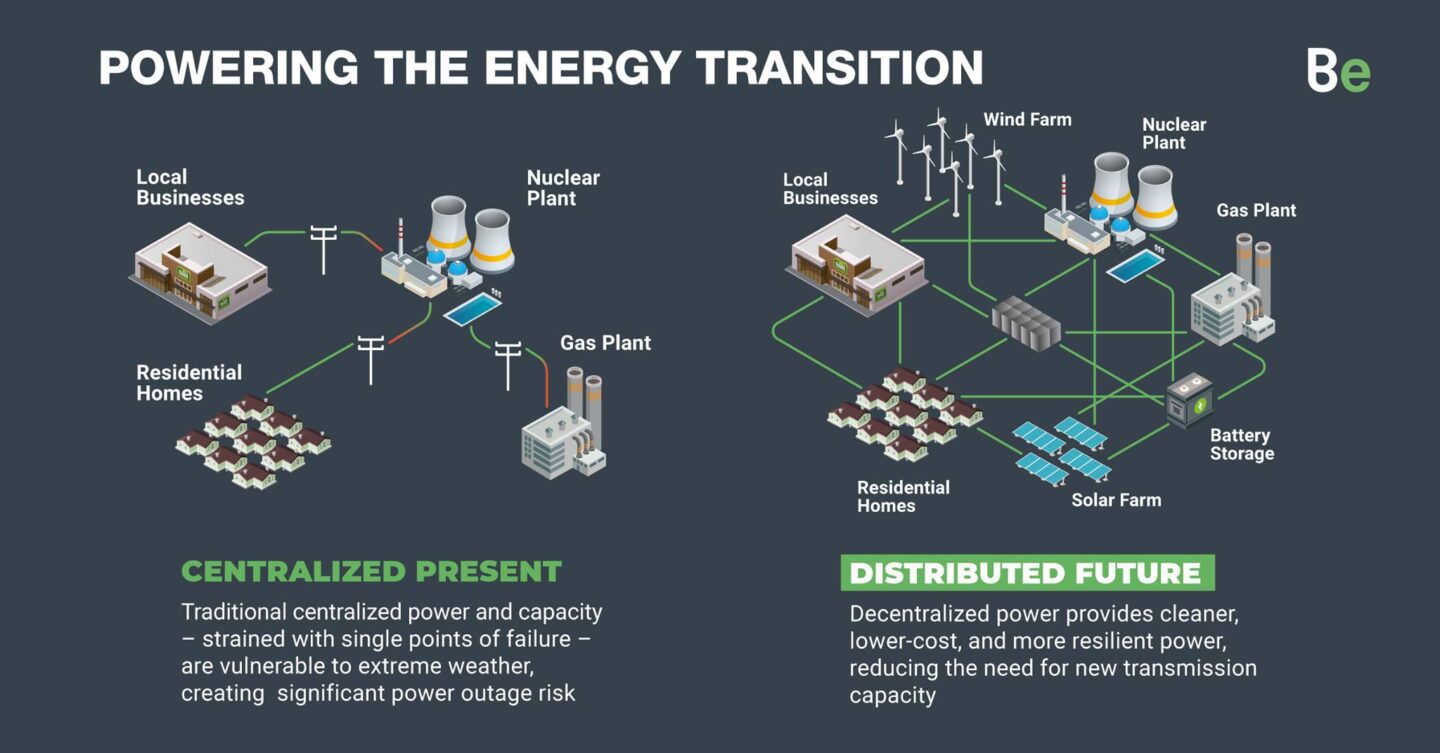
The graph above, made by Bloom Energy, shows the difference between the actual, traditional centralized present in contrast to the ‘distributed future’
Conclusion
Decentralized energy plays a vital role in the energy industry, promoting sustainability, resilience, and local empowerment. By adopting decentralized systems, communities can achieve greater control over their energy sources and contribute to a more sustainable future. Explore the possibilities of decentralizing energy and discover how it can reshape the energy landscape.
Frequently asked questions
What is decentralized energy?
It refers to localized energy production and distribution systems that are closer to the point of consumption. It involves generating energy from diverse sources, such as renewables, combined heat and power (CHP), and microgrids. This approach promotes efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
What are the benefits of decentralized systems?
- Sustainability: It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and supports the transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Resilience: Localized energy systems enhance resilience by minimizing the impact of grid failures, natural disasters, or disruptions, ensuring continued access to energy.
- Local Empowerment: Decentralization of energy empowers communities, enabling them to participate in energy production, make informed decisions, and reap economic and social benefits.
How does decentralized energy contribute to a sustainable future?
Decentralizing energy plays a crucial role in achieving a sustainable future:
- Renewable Energy Integration: It facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and biomass. This helps reducing carbon emissions and promoting environmental preservation.
- Energy Efficiency: by minimizing transmission and distribution losses. Optimizing, like this, energy consumption, and enabling local energy management.
- Community Engagement: empowers communities to take an active role in shaping their energy future. Resulting in fostering local economic development, and enhancing energy security.






