Welcome to our comprehensive guide on distributed generation in the energy industry. In this guide, we will explore its concept, its role in enabling localized energy production, and its various applications across different sectors. Join us as we delve into its benefits and potential.
Understanding Distributed Generation
Distributed generation refers to the production of electricity from multiple smaller-scale energy sources located close to the point of consumption. It decentralizes the energy generation process, reducing the need for long-distance transmission and promoting energy self-sufficiency.
Benefits and Applications of Distributed Generation
Some benefits and applications are:
Localized Energy Production: By generating electricity closer to where it is consumed, distributed systems reduce transmission losses and increases overall system efficiency. It allows communities, businesses, and institutions to have greater control over their energy supply.
Grid Resilience and Reliability: Communities that enjoy a distributed system, can enhance their grid resilience. This also helps in reducing the risk of widespread power outages. Localized energy sources can continue to operate during disruptions, ensuring reliable electricity supply to critical infrastructure, emergency services, and residential areas.
Renewable Energy Integration: Generation in a distributed manner facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and small-scale hydroelectric systems. It enables the efficient utilization of clean energy resources and supports the transition to a more sustainable energy mix.
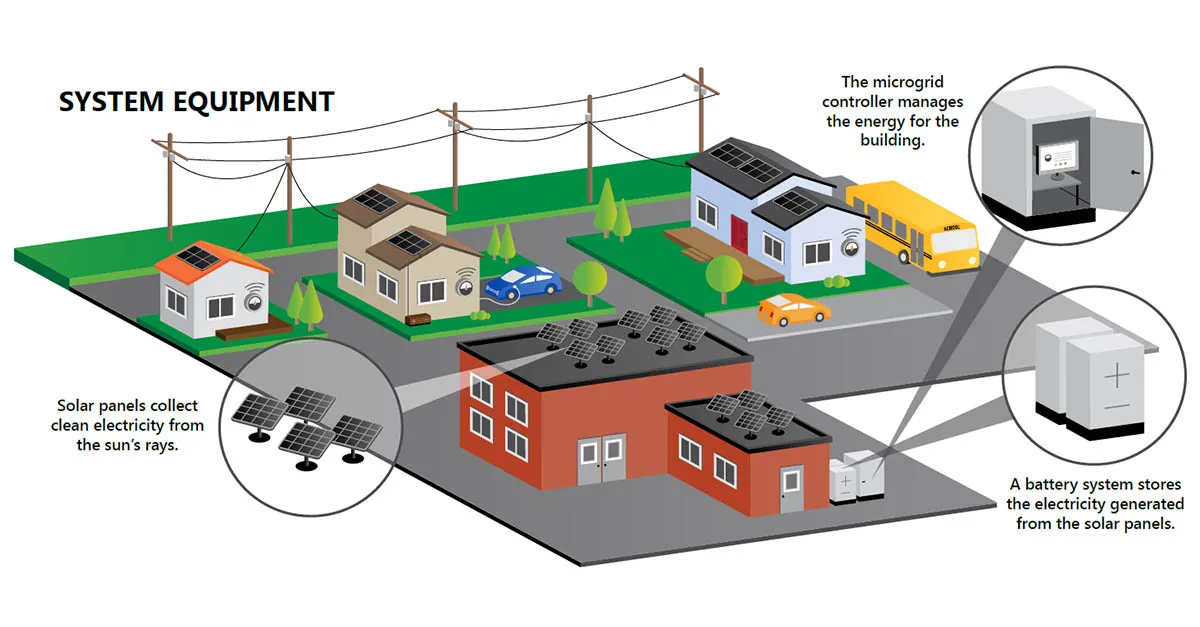
The illustration above, made by FranklinWH, shows how a microgrid functions to provide power to a community. In this case, the microgrid gets power from a renewable energy source: solar panels.
Conclusion
Distributed generation plays a vital role in the energy industry, enabling localized energy production, enhancing grid resilience, and promoting renewable energy integration. By adopting distributed systems, communities can achieve greater energy self-sufficiency and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Frequently asked questions
What is distributed generation?
It refers to the production of electricity from smaller-scale energy sources located close to where it is consumed. It promotes energy self-sufficiency, reduces transmission losses, and enhances grid resilience.
How does distributed generation benefit the energy industry?
The energy industry benefits as follows:
- Localized Energy Production: It allows communities and businesses to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on centralized power plants and increasing energy independence.
- Grid Resilience: Enhancing the resilience of the energy grid by providing backup power during outages and reducing the risk of widespread blackouts.
- Renewable Energy Integration: It enables the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into the existing energy infrastructure, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix.
What are some examples of distributed generation technologies?
Various technologies are used in distributed generation:
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: These convert sunlight into electricity and are commonly installed on rooftops or in solar farms.
- Small Wind Turbines: They harness the power of wind to generate electricity, suitable for both residential and commercial use.
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: These systems simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat, maximizing energy efficiency.






