Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years as a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation. This glossary entry provides an in-depth understanding of an electric vehicle, their components, benefits, and their role in reducing carbon emissions.
What is an Electric Vehicle (EV)?
An electric vehicle, commonly known as an EV, is an automobile powered by one or more electric motors. Unlike conventional vehicles that rely on internal combustion engines, EVs utilize electricity stored in batteries or fuel cells to generate power and propel the vehicle. EVs come in various types, including all-electric, hybrid, and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
How do Electric Vehicles Work?
EVs are powered by electric motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. These motors are powered by batteries, which store electricity. The most common type of battery used in EVs is lithium-ion, known for its high energy density and long life. Other battery technologies, such as nickel-metal hydride and solid-state batteries, are also used in certain EV models.
Owning electric vehicle comes with numerous benefits compared to conventional vehicles. One of the key advantages is their positive impact on the environment. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality. Additionally, EV owners enjoy cost savings due to lower fuel and maintenance expenses. These vehicles are also more energy-efficient, converting a higher percentage of energy into propulsion compared to internal combustion engine vehicles.
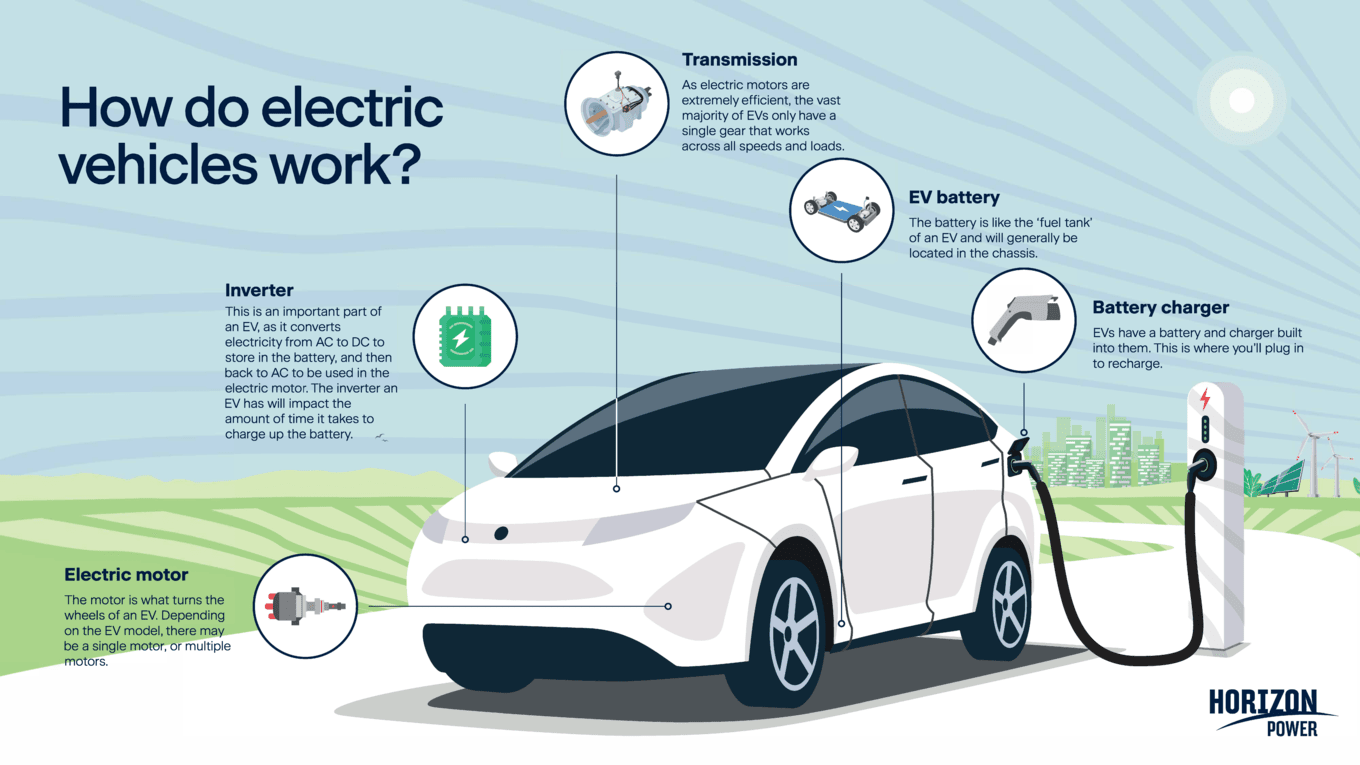
The illustration above, made by Horizon Power, shows how an EV works.
Types of Electric Vehicles:
All-Electric Vehicles (AEVs): All-electric vehicles, also known as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), rely solely on electricity for propulsion. They are powered by a large battery pack that is recharged by plugging into an electric charging station. AEVs offer zero tailpipe emissions and have the potential for longer driving ranges as battery technology continues to advance.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Hybrid EVs combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor. The engine and motor work together to optimize fuel efficiency, with the electric motor assisting during acceleration and regenerative braking. HEVs do not need to be plugged in as they self-charge through the engine and regenerative braking.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Plug-in hybrid EVs have both an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. They can be charged from an external power source, such as a charging station, and also self-charge through regenerative braking and the engine. PHEVs offer the flexibility of running on electricity alone for shorter trips or utilizing the combustion engine for longer journeys.
The Future of Electric Vehicles
Technological Advancements: The future of electricity vehicles holds exciting technological advancements. Battery technology is continuously improving, leading to longer ranges, faster charging times, and increased energy efficiency. Researchers are exploring new battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries, to overcome existing limitations and further enhance EV performance.
Infrastructure Development: To support the widespread adoption of this type of vehicles, the expansion of charging infrastructure is crucial. Governments and private companies are investing in the installation of public charging stations, fast-charging networks, and home charging solutions. These developments aim to alleviate range anxiety and provide convenient charging options for EV owners.
Environmental Impact: EVs play a vital role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. As the electricity grid shifts towards renewable energy sources, EVs become even greener in terms of their overall carbon footprint. By transitioning from fossil fuel-powered vehicles to electric vehicles, we can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the transportation industry, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional vehicles. As we strive for a greener future, EVs play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions, improving air quality, and promoting energy efficiency. The advancements in battery technology, coupled with the expansion of charging infrastructure, are driving the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
By embracing electric vehicles, we can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable world. The electric grid, with its renewable energy sources, supports the growth of EVs and further enhances their environmental benefits. As technology continues to evolve, these vehicles are becoming more accessible, affordable, and practical for everyday use.
Frequently asked questions
What is an electric vehicle?
An electric vehicle, also known as an EV, is a type of vehicle that runs on electricity stored in its batteries. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, electric vehicles use electric motors to propel themselves, resulting in zero tailpipe emissions.
How far can electric vehicles travel on a single charge?
The driving range of an electric vehicle can vary depending on several factors, such as the vehicle model, battery capacity, driving conditions, and weather. On average, modern electric vehicles can travel between 100 to 300 miles on a single charge, with some models offering even longer ranges.
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
The charging time for an electric vehicle depends on the charging equipment used and the vehicle’s battery capacity. Charging at home using a standard wall outlet can take several hours, while using a dedicated Level 2 charging station can reduce the charging time to a few hours. Fast-charging stations, available in public locations, can provide a significant charge in as little as 30 minutes.






