The term “electrification” refers to the process of transitioning various sectors and industries from traditional fuel-based systems to electric-powered technologies. This comprehensive glossary entry will explore the concept of electrification in the energy industry, its significance, applications, and its role in shaping a sustainable and efficient future. Read on to gain a clear understanding of electrification and its impact on our daily lives.
What is Electrification?
Electrification is the process of integrating electric power into various sectors such as transportation, heating, cooling, and industrial processes, which were traditionally dependent on fossil fuels or other non-electric sources. It involves the adoption of electric technologies to enhance energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainability.
The Importance of Electrification:
1. Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced Emissions: Electrification plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by reducing carbon emissions. Electric-powered technologies produce zero or significantly lower emissions compared to their fossil fuel counterparts.
- Air Quality Improvement: By shifting away from fossil fuels, being electrified helps to improve local air quality, reducing pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides.
2. Energy Efficiency and Conservation:
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Electric technologies, such as electric vehicles and heat pumps, have higher energy efficiency compared to conventional systems, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower energy costs.
- Demand-Side Management: Electrification enables better management of energy demand by leveraging advanced control systems and smart grid technologies, optimizing energy usage and reducing peak demand.
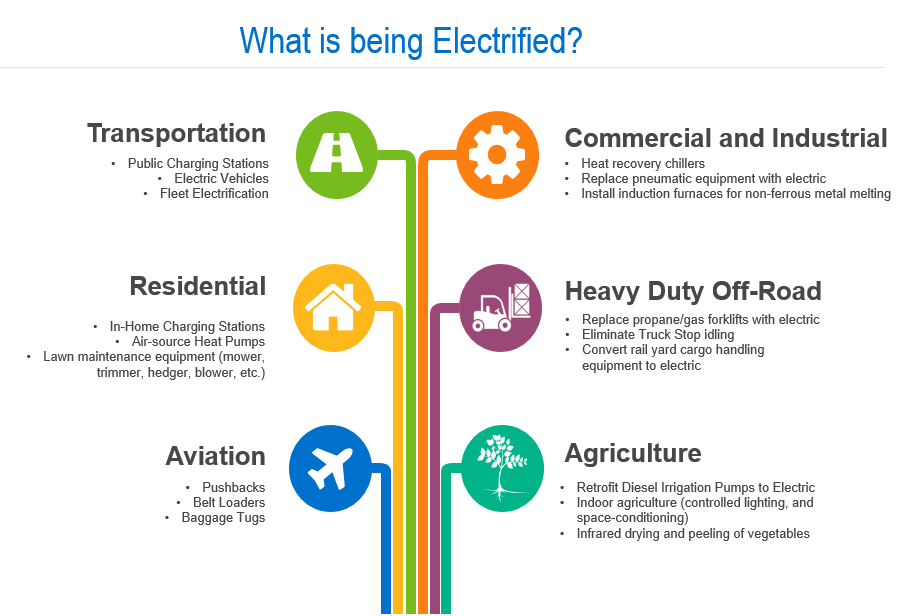
The illustration above, made by Resource Innovators, shows the different sectors that can be electrified for a more sustainable future.
Applications of Electrification:
1. Transportation:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The adoption of electric vehicles is a key driver in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. EVs offer a sustainable alternative for personal and public transportation.
- Charging Infrastructure: The development of a robust charging infrastructure network is crucial for supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
2. Residential and Commercial Buildings:
- Electrified Heating and Cooling: Electric heat pumps provide efficient heating and cooling solutions, replacing traditional fossil fuel-based systems like furnaces and boilers.
- Smart Home Energy Management: Integration of smart home technologies that optimize energy consumption, improve comfort, and reduce energy waste.
3. Industrial Processes:
- Electrified Industrial Equipment: Replacing fossil fuel-powered machinery and equipment with electric alternatives helps reduce emissions and increase operational efficiency in various industries.
- Process Heat Electrification: Electrifying industrial processes that require high-temperature heat, such as in manufacturing or chemical industries, can contribute to decarbonization efforts.
Future Trends and Innovations:
- Grid Modernization: Electrification requires a resilient and flexible electric grid capable of handling increased electricity demand. Grid modernization initiatives focus on integrating renewable energy sources, implementing energy storage solutions, and adopting advanced grid management technologies.
- Electrification in Developing Countries: Expanding efforts in developing countries can have a transformative impact, providing access to clean energy, improving healthcare, education, and economic opportunities.
Conclusion
Electrification is revolutionizing the energy landscape by paving the way for sustainable, efficient, and clean energy systems. From transportation to residential and industrial sectors, the adoption of electric-powered technologies offers significant environmental and economic benefits. As the world transitions towards a low-carbon future, electrification plays a crucial role in reducing emissions, improving energy efficiency, and creating a more sustainable planet.
Frequently asked questions
What is electrification?
Electrification refers to the process of transitioning various sectors of the economy. Such sectors atr transportation, buildings, and industries, from using fossil fuels to utilizing electricity. It involves adopting electric vehicles, electrified heating and cooling systems, and electrically powered machinery. This to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability.
How does electrification benefit the environment?
By playing a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. By embracing electricity generated from renewable sources, being electrified significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This transition helps improve air quality, mitigate the impacts of climate change, and create a cleaner and healthier environment for all.
What are the key challenges and opportunities in electrification?
Electrifying various sectors presents both challenges and opportunities. Some challenges include the need for infrastructure development, such as charging stations for electric vehicles, and upgrading grid systems to handle increased electricity demand. However, electrification also brings opportunities for innovation, job creation, and energy efficiency improvements. It fosters technological advancements, promotes renewable energy integration, and accelerates the transition to a more sustainable energy future.






