Energy storage involves accumulating excess electricity during times of high production and storing it for later use when demand is high or production is limited. This ensures a reliable and continuous energy supply, addressing the intermittency issues associated with renewable energy sources.
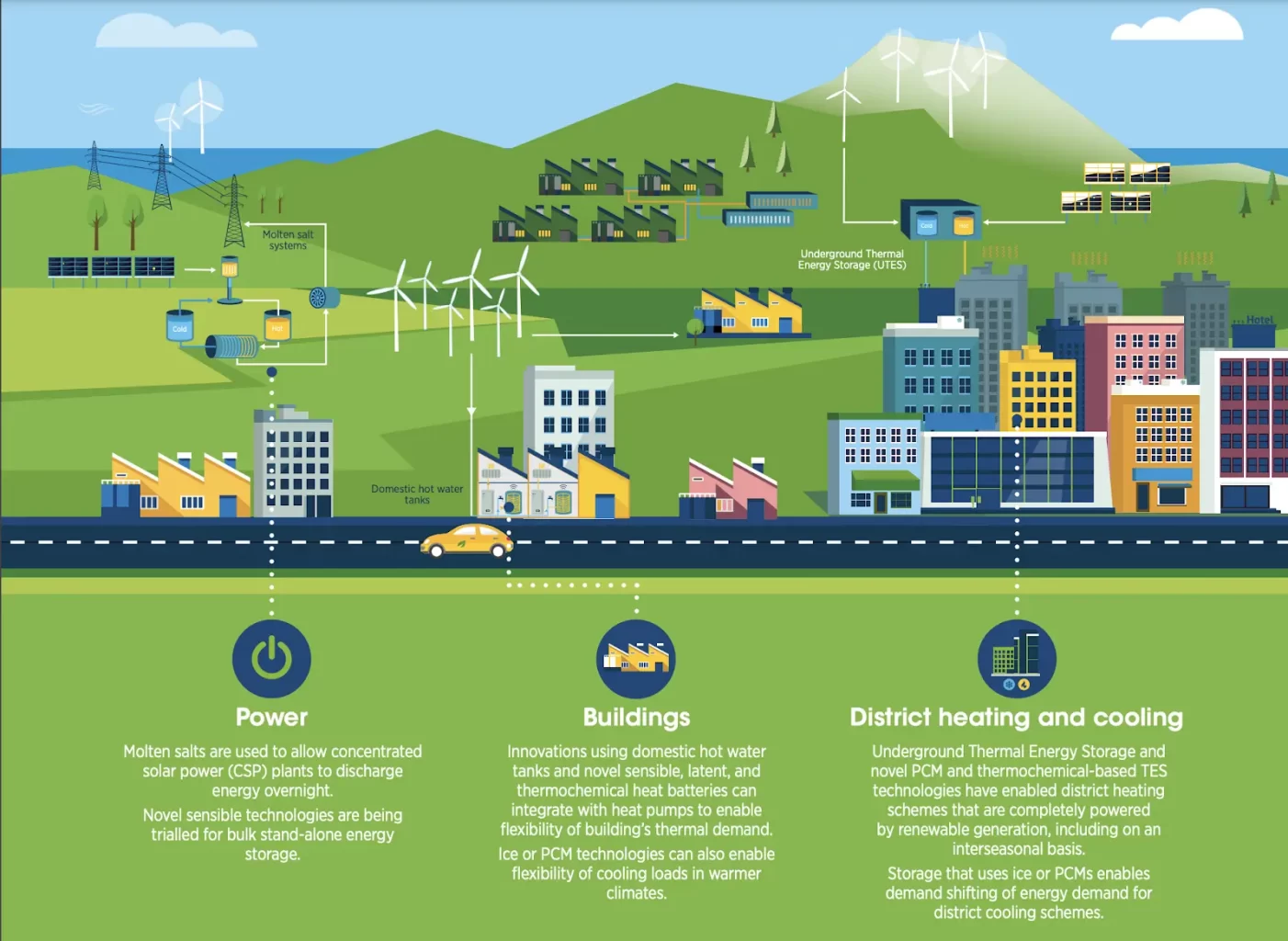
Thermal energy technologies allow renewable energy to be stored and used later for heating and cooling. Image: Innovation Outlook: Thermal Energy Storage, IRENA
Technologies for energy storage
Various technologies facilitate the practice of storing energy, each with its unique characteristics. Common technologies include:
Battery Storage
Utilizing electrochemical cells to store and release energy, commonly found in applications such as electric vehicles and grid-scale storage.
Pumped Hydro Storage
Using the gravitational potential energy of water by pumping it to an elevated reservoir during low-demand periods and releasing it to generate electricity during high-demand periods.
Flywheel Energy Storage
Employing a rotating mass (flywheel) to store kinetic energy, which is converted back to electricity when needed.
Thermal Energy Storage
Storing energy in the form of heat or cold for later use, commonly used in solar thermal power plants and heating applications.
Importance of Energy Storage
Storing energy plays a crucial role in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of the power grid, particularly as the world shifts towards renewable power sources. It acts as a buffer, allowing for the storage of surplus power generated during periods of high production and low demand, and releasing it during shortages or peak consumption times. See below some important aspects of it.
Grid Stability
It significantly contributes to grid stability by buffering imbalances between production and consumption. It manages fluctuations, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply.
Integration of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can be intermittent. Storing energy allows excess generated power to be captured when production is high and released when demand exceeds supply, promoting the seamless integration of renewables into the grid.
Emergency Backup
This systems are essential for emergency backup solutions, providing a quick and dependable power source during outages to support critical infrastructure and essential services.
Challenges and Innovations
Energy storage represents a significant challenge in the transition to renewables due to its complexity and necessity. As renewable energy generation like solar and wind is intermittent, meaning it doesn’t produce power consistently, there’s a pressing need to store excess energy when production is high and demand is low. Some factors include
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development in technologies aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance. Advancements in battery chemistry, for instance, contribute to increased energy density and longer cycle life.
Economic Viability
The economic feasibility of storing energy solutions remains a crucial consideration. Innovations in financing models and regulatory frameworks are necessary to make projects economically viable and appealing to investors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, energy storage is crucial by providing a resilient, reliable, and sustainable power supply. Existing technologies support the integration of renewable energy and provide emergency backup solutions, playing a vital role in shaping the future of energy systems. As technology advances, storing energy will remain a key enabler of a more efficient and sustainable energy landscape.
Frequently asked questions
How does energy storage contribute to grid stability?
Energy storage is crucial for maintaining grid stability by buffering imbalances between energy production and consumption. It manages fluctuations, ensuring a steady power supply and enhancing the overall stability of the electrical grid.
What are the common technologies used for energy storage?
Various technologies facilitate energy storage, including:
Battery Storage: Utilizes electrochemical cells for storing and releasing energy, Pumped Hydro Storage: Uses gravitational potential energy of water, Flywheel Energy Storage: Stores kinetic energy in a rotating mass, Thermal storage: Stores energy in the form of heat or cold.
How does energy storage contribute to emergency backup solutions?
During power outages, the systems storing energy provide a fast and reliable source of power to support critical infrastructure and ensure the continuity of essential services.






