Fossil fuels are a crucial component of modern energy production, originating from organic matter that accumulated over millions of years. They have been the primary source of energy for industrial, transportation, and residential purposes. However, the usage presents significant environmental challenges due to their carbon-intensive nature and contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
What Are Fossil Fuels?
The decomposition of organic matter buried beneath the Earth’s surface over geological time periods produces energy sources known as fossil fuels. The three primary types are:
Coal, the first type of fossil fuel, forms from the remains of plant matter that accumulated in swampy environments over millions of years.
The second type is oil (Petroleum). It is derived from the organic remains of marine organisms buried in sedimentary rock layers.
The third type is natural gas. Comprised primarily of methane, formed from the decomposition of organic matter under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Usage and Applications
People have extensively utilized fossil fuels for various purposes, including:
Electricity Generation: Coal, oil, and natural gas are widely used in power plants to generate electricity.
Transportation: Oil-based fuels power vehicles, airplanes, and ships, facilitating transportation and mobility.
Industrial Processes: It serve as feedstocks for manufacturing processes, including petrochemicals and plastics production.
Residential Heating: Oil and natural gas are commonly used for residential heating and cooking purposes.
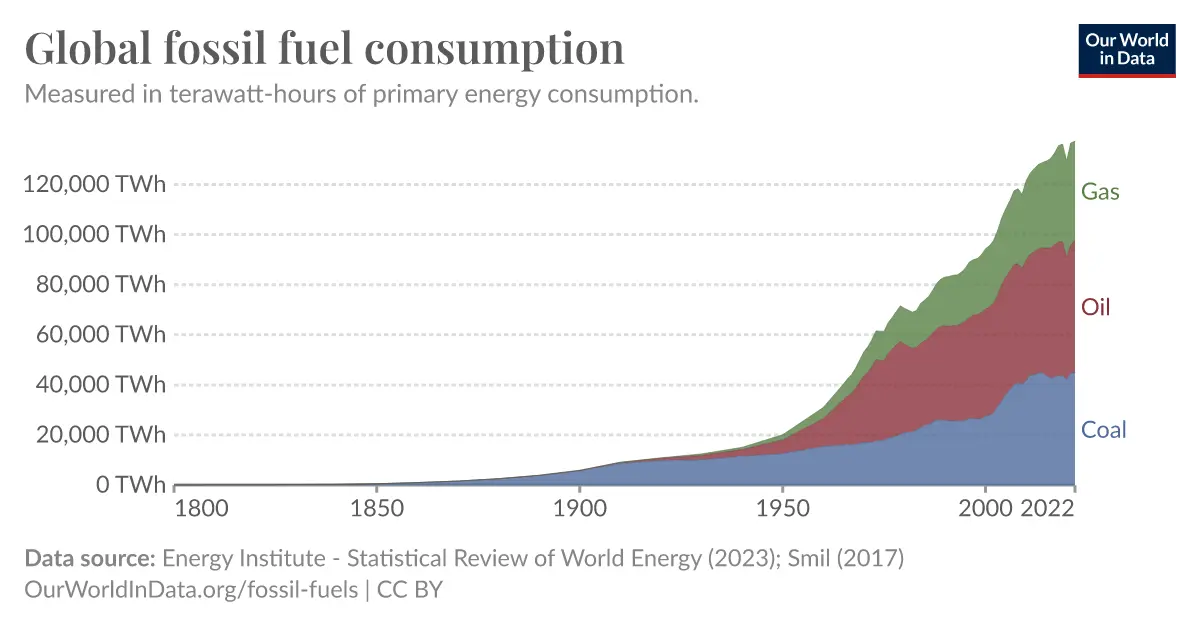
Global fossil fuel consumption. Source.
Environmental Impact
Despite their widespread use, they pose significant environmental challenges, including:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Combustion of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming and climate change.
Air Pollution
Burning fossil fuels emits pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, leading to air quality degradation and adverse health effects.
Resource Depletion
Fossil fuel extraction and consumption contribute to the depletion of finite natural resources and environmental degradation through activities such as mining and drilling.
Transition to Sustainable Alternatives
In response to environmental concerns and the need to address climate change, there is a global movement towards transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources and cleaner technologies. This transition involves:
Renewable Energy: Embracing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower to reduce reliance and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy efficiency measures and technologies to reduce overall energy consumption and optimize resource utilization.
Policy and Regulation: Enacting policies and regulations aimed at phasing out fossil fuel subsidies, promoting clean energy incentives, and setting emissions reduction targets.
Conclusion
Fossil fuels have been crucial in powering human civilization’s industrial and technological advancements. However, their widespread use has also contributed to environmental degradation and climate change. As society seeks to address these challenges, there is an increasing emphasis on transitioning towards sustainable alternatives and reducing dependence. By embracing renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and implementing supportive policies, we can achieve a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Frequently asked questions
What are fossil fuels and How are they formed?
The decomposition of organic matter buried beneath the Earth’s surface over geological time periods produces energy sources in the form of fossil fuels. They include coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas.
What environmental challenges are associated with fossil fuels?
Despite their widespread use, fossil fuels pose significant environmental challenges. The combustion of these fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming and climate change.
How can society transition to Sustainable Alternatives From Fossil Fuels?
This transition involves adopting renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower to decrease dependence and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, implementing energy-efficient measures and technologies can help reduce overall energy consumption and optimize resource utilization. Enacting policies and regulations to phase out fossil fuel subsidies, promote clean energy incentives, and set emissions reduction targets are crucial steps in transitioning to sustainable alternatives.






