Introduction
In the global pursuit of sustainable development and environmental responsibility, the concept of a low-carbon economy has emerged as a transformative approach. This economic system aims to reduce carbon emissions and minimize environmental impact, primarily through the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as renewables.
Transitioning to sustainable energy sources
Renewable Energy Integration
Having a lower-carbon industry relies on integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, to minimize carbon footprints. By utilizing these cleaner alternatives, the economy can decrease its reliance on fossil fuels, which are a primary source of carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency Measures
Efforts to improve energy efficiency also significantly contribute to the low-carbon paradigm. Implementing technologies and practices that optimize energy use across industries and sectors helps reduce overall energy consumption, further aligning with the principles of a low-carbon framework.
Economic and environmental benefits of a low-carbon economy
Economic Diversification
The shift towards sustainable practices can open up new industries, technologies, and job opportunities, fostering a resilient and dynamic economic landscape.
Environmental Conservation
By reducing carbon emissions, this economic model helps mitigate climate change, protects ecosystems, and preserves biodiversity.
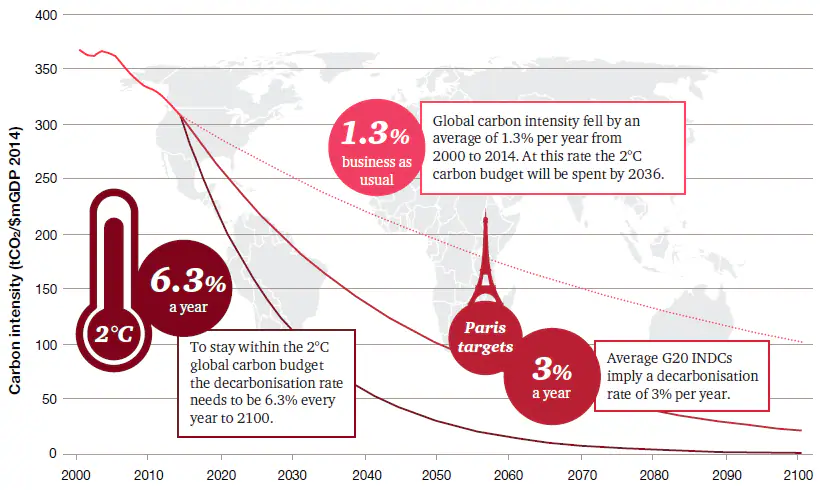
The current state of the transition towards a low-carbon economy. Source.
Challenges and considerations for a low-carbon economy
Technological Transition
The transition requires significant technological advancements. It is imperative to invest in research, development, and the widespread adoption of innovative technologies to overcome this challenge.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Effective policies and regulatory frameworks are crucial to drive the transition. Governments and international bodies play a vital role in creating an environment that incentivizes low-carbon practices and penalizes carbon-intensive activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of a Low-Carbon Economy represents a visionary approach to economic development. By reducing carbon emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and embracing sustainable practices, societies can build a more resilient, environmentally friendly, and economically vibrant future. Global awareness and commitment to sustainability is growing. With this, a lower carbon industry stands for a more balanced and harmonious coexistence with our planet.
Frequently asked questions
What is the core principle behind a Low-Carbon Economy?
It focuses on reducing carbon emissions and minimizing environmental impact. This is primarily achieved by transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as renewables, as a fundamental shift away from carbon-intensive practices.
What are some economic benefits associated with pursuing a Low-Carbon Economy?
Economic diversification can be achieved by pursuing a low-carbon economy. The shift towards sustainable practices opens up new industries, technologies, and job opportunities, fostering a resilient and dynamic economic landscape that is less dependent on traditional, carbon-intensive sectors.
How does a Low-Carbon Economy contribute to environmental conservation?
The key benefit of a low-carbon economy is its positive impact on the environment. By reducing carbon emissions, this economic model helps to mitigate climate change, protect ecosystems, and preserve biodiversity.






