A microgrid is a self-contained energy system that can generate, distribute, and control electricity locally. Unlike traditional centralized power grids, microgrids are smaller in scale and can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. They consist of a combination of energy sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and fossil fuel generators, along with energy storage systems and advanced control technologies.

How do microgrids work?
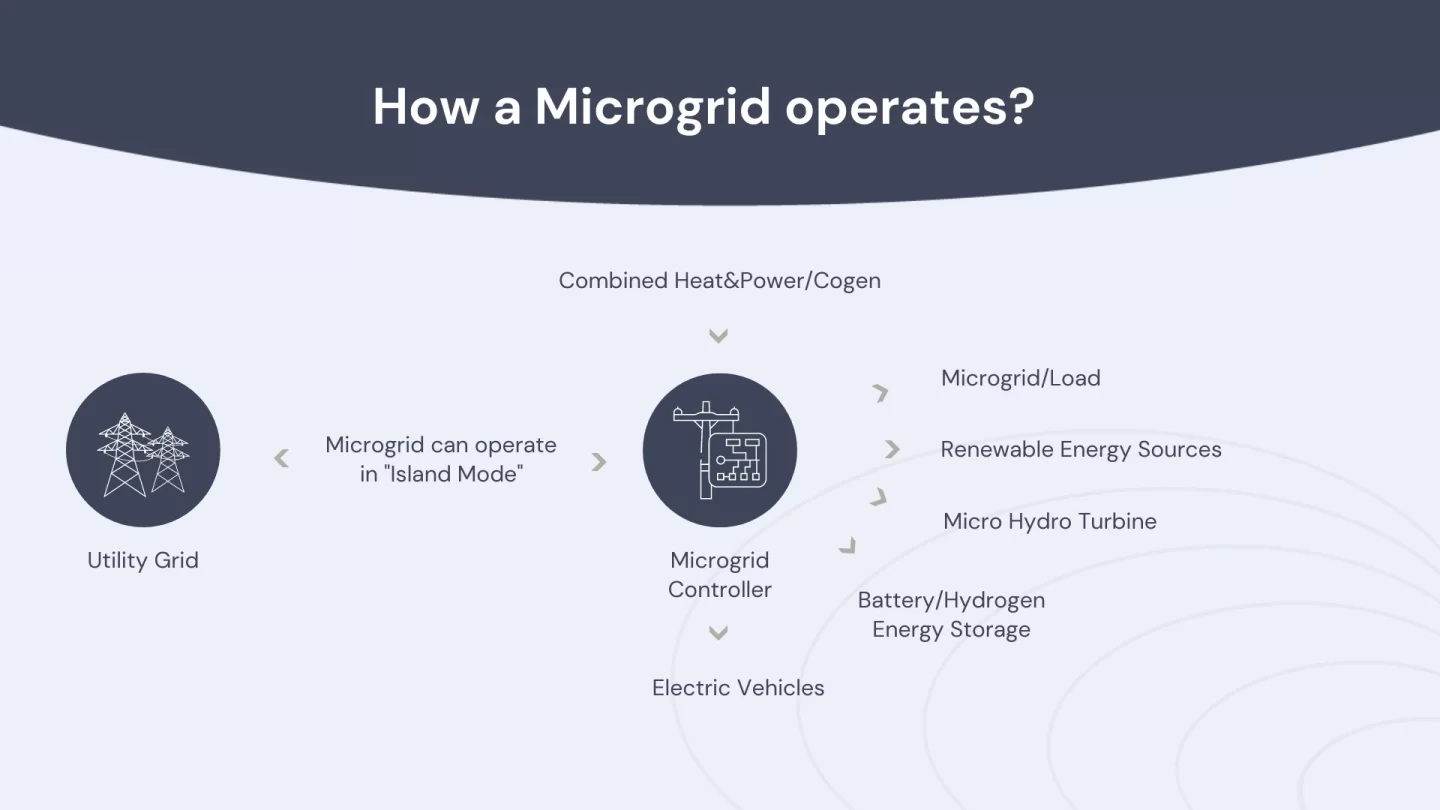
How a microgrid operates. Source.
Microgrids operate by utilizing a diverse mix of energy generation sources and storage technologies to meet local energy demand. They can function autonomously, disconnected from the main grid, or synchronize with the grid to exchange power as needed. Microgrid controllers manage energy flow and distribution, optimizing system operation for reliability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
Benefits of microgrids
Microgrids provide numerous advantages, enhancing energy resilience, efficiency, and sustainability. They enable independent operation from the main power grid, facilitate the integration of renewable resources, and offer significant cost savings and improved grid stability, particularly in remote locations.
Improve Energy Resilience
Additionally, they improve energy resilience by providing localized power generation and distribution capabilities. In areas prone to grid outages or natural disasters, a microgrid can continue to supply electricity to key infrastructure such as hospitals, emergency services, and community centers, ensuring uninterrupted operations during times of crisis.
Integration of Renewable Energy
Many microgrids prioritize integrating renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, combating climate change and contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
Moreover, microgrids can potentially save costs and improve efficiency by optimizing energy generation and distribution at the local level. They minimize transmission losses associated with long-distance power delivery and leverage energy storage technologies to store excess generation for later use. This reduces overall energy costs and improves system efficiency.
Applications of microgrids
They prove essential in enhancing energy security, supporting sustainability, and providing reliable power in remote areas. They are particularly valuable in integrating renewable energy, improving grid stability, and enabling communities and businesses to manage energy independently.
Remote Communities
Microgrids are an ideal solution for remote communities or areas with limited access to centralized power infrastructure. In off-grid or underserved regions, microgrids offer a dependable and sustainable energy source, promoting economic development, enhancing quality of life, and strengthening community resilience.
Industrial and Commercial Facilities
Industrial and commercial facilities frequently use microgrids to ensure a reliable power supply and minimize the impact of grid disruptions on critical operations. Microgrids provide businesses with greater control over their energy supply, reducing the risk of downtime, productivity losses, and revenue impacts associated with power outages.
Military Installations
Military bases and installations use microgrids to improve energy security and operational readiness. Self-sufficient energy systems reduce dependence on vulnerable external power sources, improve mission readiness, and enhance overall resilience in challenging environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, microgrids offer localized, resilient, and sustainable power solutions for various applications. They represent a transformative approach to energy management. By integrating renewable energy sources, energy storage technologies, and advanced control systems, microgrids are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of the global energy landscape. This fosters energy independence, security, and environmental sustainability.
Frequently asked questions
What is a Microgrid and How Does It Work?
It is a localized energy system that generates, distributes, and controls electricity independently or with the main grid. It operates using a mix of energy sources and storage technologies to meet local energy demand efficiently and sustainably.
Where Are Microgrids Commonly Used?
Remote Communities: Providing reliable energy access in off-grid areas.
Industrial and Commercial Facilities: Ensuring continuous operations and minimizing downtime.
Military Installations: Enhancing energy security and operational readiness.
How Do Microgrids Contribute to Energy Sustainability?
Microgrids promote energy independence, security, and environmental sustainability by integrating renewable energy sources, optimizing energy usage, and enhancing resilience against grid disruptions.






