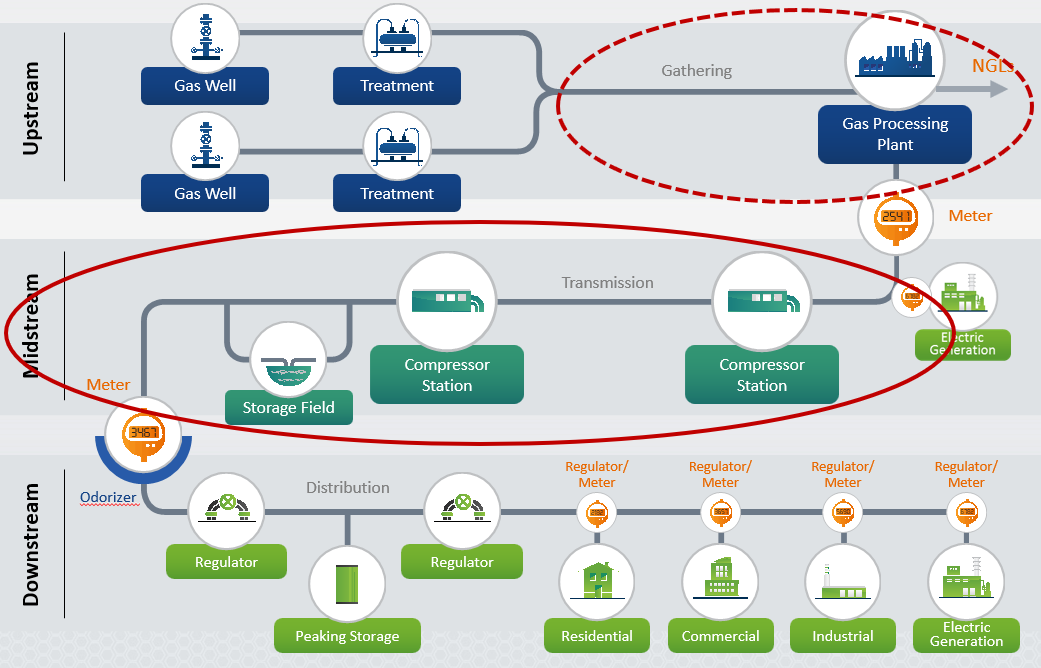
The midstream energy industry plays a crucial role in the energy value chain. It is responsible for the transportation, storage, and distribution of crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products. Companies build and operate the infrastructure necessary to move energy resources from their source to processing plants, refineries, and end-users.
What is Midstream Energy?
The industry is one of the three major components of the energy industry, alongside upstream and downstream. Midstream activities primarily involve the transportation and storage of crude oil, natural gas, and other products. Operations are necessary to connect producers and refiners, as well as to transport energy resources to end-users.
Operations in the Midstream Energy Industry
The midstream energy industry is responsible for several critical operations that enable the transportation and storage of energy resources. Some of the key operations include:
- Gathering: Gathering involves the collection of crude oil and natural gas from wells and the transportation of these resources to processing facilities.
- Transportation: Transportation involves the movement of energy resources, such as crude oil and natural gas, over long distances using pipelines, tankers, and trucks.
- Storage: Storage involves the preservation of crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products in storage tanks, underground caverns, and salt domes.
- Processing: Processing involves the conversion of crude oil and natural gas into refined products such as gasoline, diesel fuel, and petrochemicals.
Key Challenges in the Midstream Energy Industry
These several challenges impact operations and profitability:
- Regulatory Compliance: There is heavy regulation by federal and state agencies, and non-compliance with these regulations can lead to significant fines and penalties.
- Environmental Concerns: such as spills, leaks, and emissions. These environmental concerns can lead to reputational damage and financial losses.
- Infrastructure Investment: The midstream industry requires significant investment in infrastructure, such as pipelines and storage tanks, which can be costly and take years to build.
- Market Volatility: such as fluctuations in oil and gas prices, which can impact profitability.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements, such as renewable energy, can reduce the demand for traditional energy sources, which can impact the midstream industry’s long-term viability.
Conclusion
The midstream energy industry plays a critical role in the energy value chain. It is responsible for the transportation, storage, and distribution of crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products. While the industry faces several challenges, it continues to evolve to meet the changing energy needs of the world. The industry’s ability to invest in infrastructure, comply with regulations, and adopt new technologies will be crucial to its long-term success.
Frequently asked questions
What is the midstream energy industry, and what are its operations?
The midstream energy industry is responsible for the transportation, storage, and distribution of crude oil, natural gas, and other petroleum products. Its operations include gathering, transportation, storage, and processing of energy resources.
What are the key challenges faced by the midstream energy industry?
The midstream energy industry faces several challenges such as regulatory compliance, environmental concerns, infrastructure investment, market volatility, and technological advancements.
Why is the midstream energy industry important in the energy value chain?
The midstream energy industry plays a crucial role in connecting producers and refiners and moving energy resources to end-users. Its operations enable the transportation and storage of energy resources, which is necessary to meet the changing energy needs of the world.