Introduction
Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) is a key player in the global transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. VRE includes renewable energies, such as wind and solar power, which generate electricity intermittently based on environmental conditions. This article explores VRE, highlighting its intermittent nature and its crucial role in shaping modern energy systems.
The intermittent nature of variable renewable energy (VRE)
Wind Turbines
Wind turbines convert wind’s kinetic energy into electricity. However, the variable wind speed poses challenges in maintaining consistent energy output. Efficiently managing this intermittency is crucial for effective utilization of wind power in the energy grid.
Solar Power
Solar panels use sunlight to generate electricity, but their effectiveness depends on daylight availability and weather conditions. The intermittent nature of solar power requires strategic planning to address fluctuations and ensure a reliable energy supply.
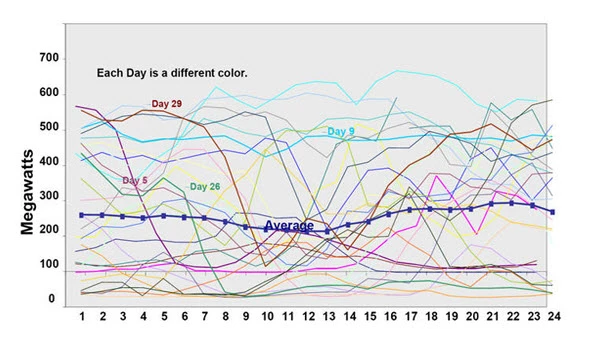
The graph above shows the variability of solar energy. Each colored line represents a day with the blue line being the average. Greentech Media, “20 PowerPoint Slides That Shook The Earth” Source
Managing variability in variable renewable energy (VRE)
Two key strategies are energy storage systems and smart grid technologies with demand response mechanisms. Smart grid technologies and demand response mechanisms help balance the intermittent nature of VRE, enhancing overall grid stability and reliability.
The Role of Energy Storage Systems in variable renewable energy
In order to effectively manage the variability of VRE sources, innovative solutions are required, with energy storage systems playing a pivotal role. These systems store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it during low-production or high-demand periods. This approach helps balance the intermittent nature of VRE, enhancing grid stability and reliability.
Smart grid technologies and demand response for variable renewable energy
To manage the variability of VRE sources effectively, innovative solutions are necessary, with energy storage systems playing a pivotal role. These systems store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it during low-production or high-demand periods. This approach helps balance the intermittent nature of VRE, enhancing grid stability and reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) represents the transformative potential of harnessing wind and solar power for electricity generation. Managing the variability of these sources requires strategic planning and innovative solutions. As the world adopts VRE, integrating energy storage, smart grid technologies, and demand response mechanisms will be crucial for building a sustainable and resilient energy future. This exploration of the VRE realm represents a major stride towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy environment.
Frequently asked questions
What is Variable Renewable Energy (VRE)?
Variable Renewable Energy (VRE) refers to renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, that generate electricity intermittently based on environmental conditions.
What factors influence the intermittency of solar power within VRE?
The intermittency of solar power is influenced by factors such as daylight availability and weather conditions. Strategic planning is essential to address fluctuations and ensure a reliable energy supply from solar sources.
How can the variability of VRE be effectively managed?
Managing the variability of VRE requires innovative solutions. Energy storage systems store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it during low-production or high-demand periods. Two key strategies are energy storage systems and smart grid technologies with demand response mechanisms. Smart grid technologies and demand response mechanisms help balance the intermittent nature of VRE, enhancing overall grid stability and reliability.






