Introduction
Fuel cells represent a revolutionary leap forward in the quest for clean and efficient energy solutions. They are electrochemical devices that convert the chemical energy of a fuel, usually hydrogen, directly into electricity. This technology holds immense promise in transforming our energy landscape.
How do fuel cells work?
They operate on a simple principle. They convert the chemical energy stored in fuels, particularly hydrogen, into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. This involves the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen, typically from the air, to produce electricity, water, and heat as byproducts. Unlike traditional combustion-based power generation, fuel cells offer a cleaner and more efficient way to generate energy.
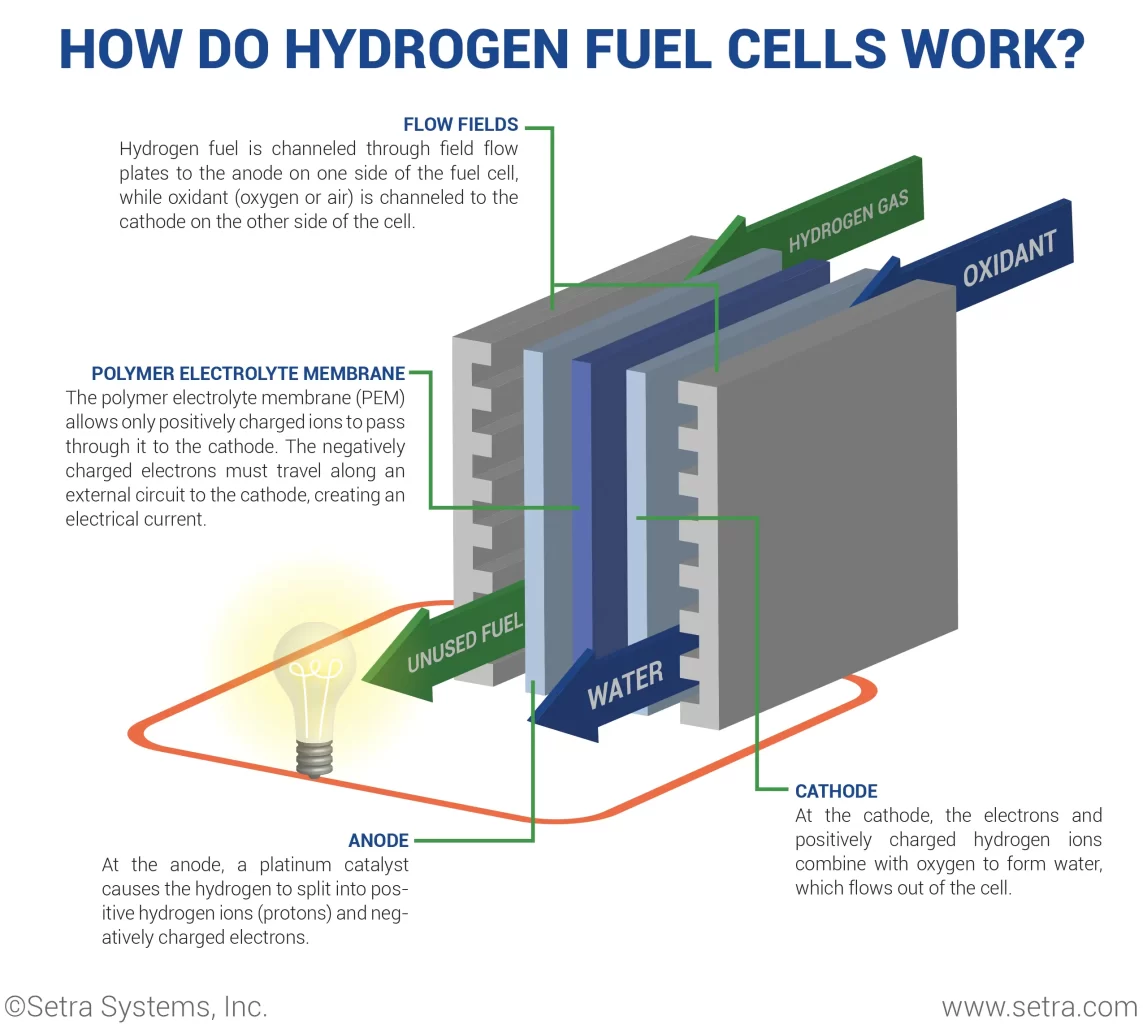
Source: What is a Hydrogen Fuel Cell? (setra.com)
The advantages of fuel cells
Utilizing Renewable Hydrogen
Fuel cells are most effective when combined with renewable hydrogen sources. Hydrogen, which is often referred to as the fuel of the future, can be produced from renewable resources such as water through processes like electrolysis. When renewable hydrogen is used as the fuel for fuel cells, the entire energy generation process becomes environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Minimal Environmental Impact
Fuel cells have a significant advantage due to their minimal environmental impact. Unlike power generation based on combustion, fuel cells produce electricity without emitting harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases. This makes fuel cells an attractive option for meeting energy demands while mitigating the impact on climate change.
Applications of Fuel Cells
These devices are versatile and efficient, making them useful in various industries and sectors. Common applications include:
Transportation
They power electric vehicles, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles emit only water vapor, contributing to cleaner air and reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
Stationary Power Generation
They are used for stationary power generation, providing a reliable and continuous source of electricity. They are often used in backup power systems for critical infrastructure such as hospitals and data centres.
Conclusion
In summary, fuel cells are at the forefront of a cleaner and more efficient energy future. Their ability to convert the chemical energy of fuels, particularly hydrogen, directly into electricity represents a revolutionary shift in our approach to power generation. The environmentally friendly nature of these devices, coupled with their versatility in applications ranging from transportation to stationary power generation, positions them as a key solution to our evolving energy needs.
Frequently asked questions
How do fuel cells differ from traditional power sources?
Fuel cells represent a departure from traditional power sources as they are electrochemical devices that convert the chemical energy of a fuel, typically hydrogen, directly into electricity. Unlike combustion-based power generation, fuel cells offer a cleaner and more efficient approach to meeting our energy needs.
What is the basic principle behind how fuel cells operate?
Fuel cells work on the simple principle of converting the chemical energy stored in fuels, particularly hydrogen, into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction. This involves the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen from the air, producing electricity, water and heat as by-products.
How can fuel cells contribute to environmental sustainability?
Fuel cells can contribute to environmental sustainability by using renewable sources of hydrogen. Often referred to as the fuel of the future, hydrogen can be sustainably produced from resources such as water through processes such as electrolysis. When renewable hydrogen is used to fuel cells, the entire energy production process becomes environmentally friendly and sustainable.






