Wind energy is a renewable source derived from the kinetic energy of wind. It is generated by wind turbines, which convert wind power into electricity through the rotation of turbine blades. Wind power is a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, making it an essential component of the global shift towards renewable sources.

How Wind Energy Works
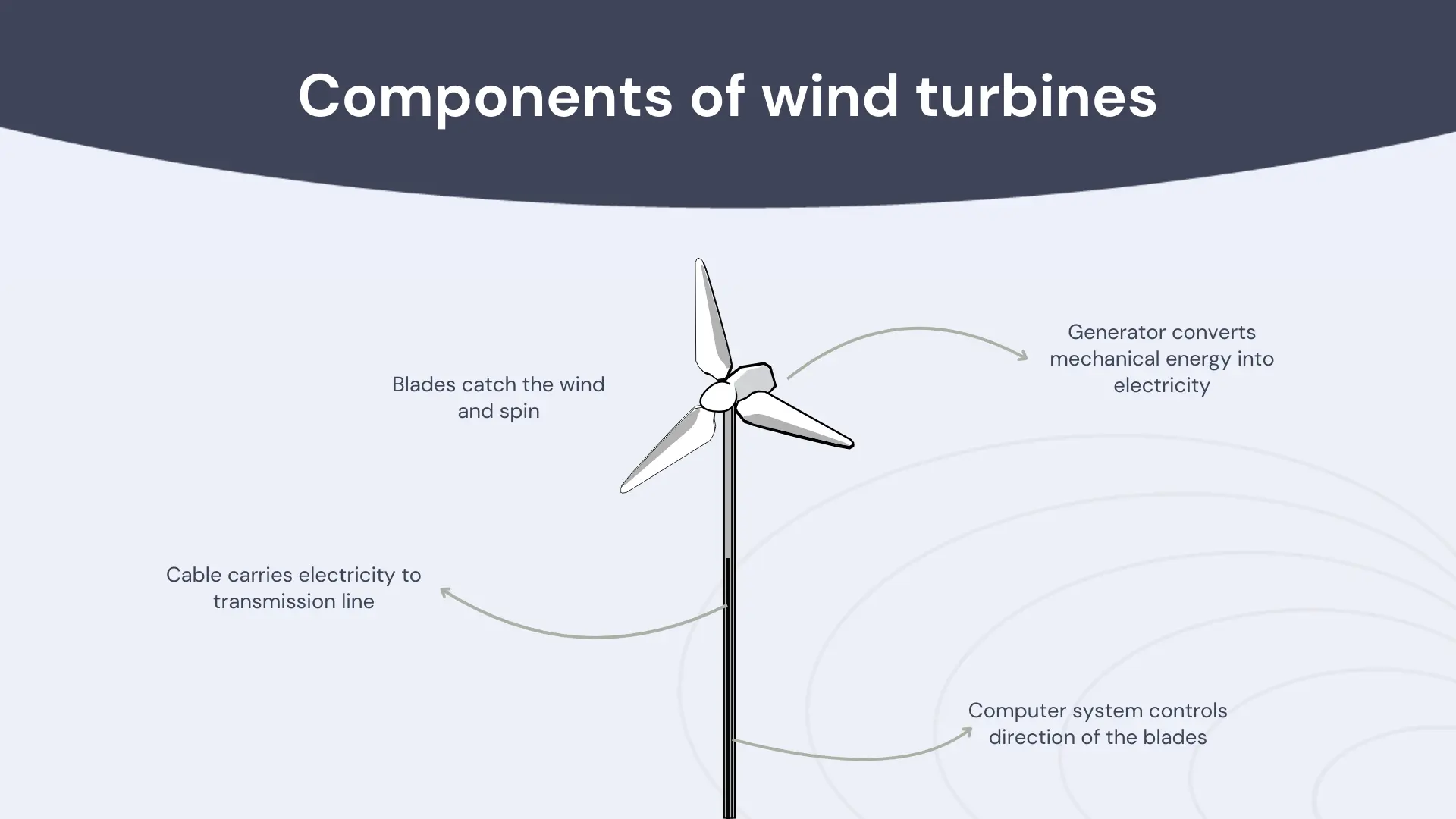
Wind turbines are built in a way in which power generation is facilitated from its different components. Source.
Wind power is generated through the following process:
Wind turbines consist of three main components: the rotor blades, the nacelle (housing the generator and gearbox), and the tower. As the wind blows, it causes the rotor blades to rotate. The rotation of the rotor blades drives the generator, which converts mechanical power into electricity. The electricity generated is then transmitted to the grid for distribution to end-users.
Prior to wind farm development, thorough wind resource assessments are conducted to identify suitable locations with consistent and strong wind speeds, maximizing production potential.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind power generation offers numerous advantages, including:
Clean and Renewable
Wind produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, making it environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Abundant Resource:
Wind is a plentiful and widespread resource that has significant potential for energy generation.
Cost-Effective
Advances in technology and economies of scale have made wind energy increasingly cost-effective, with the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) becoming competitive with conventional energy sources.
Job Creation
The wind power generation sector supports job creation and economic growth, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operations.
Challenges in Wind Energy
Despite its benefits, wind energy faces several challenges, including:
Intermittency
Power from wind is intermittent and variable, depending on wind speed and direction, which can affect grid stability and require backup power sources.
Visual and Noise Impacts
Wind turbines may face opposition due to their visual and noise impacts on landscapes and communities. Therefore, careful siting and community engagement are necessary.
Transmission Constraints
Wind farms are often located in remote areas with limited transmission infrastructure, requiring investment in grid expansion and upgrades.
Future Outlook for Wind Energy
Despite challenges, the future of wind looks promising due to ongoing technological advancements, declining costs, and supportive policy frameworks promoting renewable adoption. Power produced from wind will continue to play a vital role in the transition towards a sustainable and low-carbon future.
Conclusion
Wind power is a clean, abundant, and cost-effective renewable source that helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. With ongoing innovation and investment, wind power generation will continue to play a central role in meeting global power demand while promoting environmental stewardship and economic prosperity.
Frequently asked questions
How does wind energy work?
It is produced by wind turbines, which have rotor blades that rotate when the wind blows. This rotation powers a generator located in the turbine’s nacelle, converting mechanical energy into electricity.
What are the advantages of wind energy?
This type of energy is a clean, renewable, and abundant source of power. It produces no greenhouse gas emissions and has become increasingly cost-effective due to technological advancements and economies of scale. Furthermore, it supports job creation and economic growth in the sector.
What are the challenges facing wind energy?
The intermittency and variability of wind pose significant challenges for producing power from wind, as they affect grid stability and require backup power sources. Additionally, wind turbines can have visual and noise impacts that may lead to opposition, making careful siting and community engagement efforts necessary.






