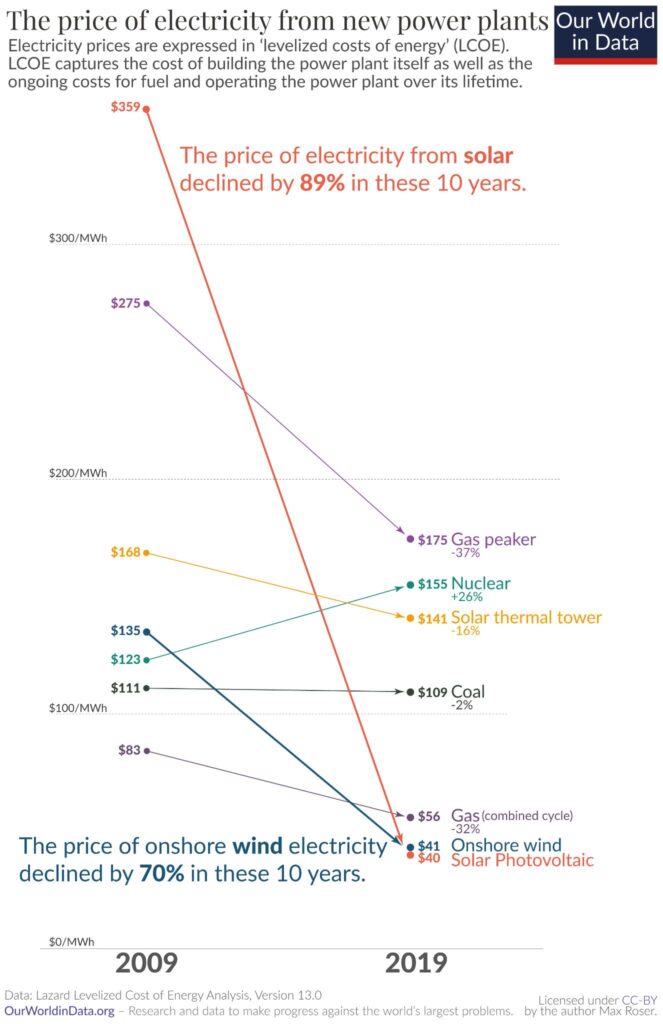
Solar energy has come a long way over the past few decades, and today it has become the cheapest source of electricity in history, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). But how did this happen? What factor or factors led to the massive reduction in solar energy prices? Let’s take a closer look.
Factor #1: Technological Advancement
One of the primary reasons for the dramatic fall in solar energy costs is the rapid improvement in solar technology. Over the years, solar panels have become more efficient, with a higher percentage of sunlight being converted into electricity. This has made solar power more cost-effective, with every watt generated costing less than before. For instance, in the early 1980s, the average cost of solar panels was around $30 per watt. Today, it is less than $0.50 per watt. That’s a 98% reduction in cost over just four decades.
In addition, advancements in manufacturing processes have allowed manufacturers to produce solar panels more efficiently, resulting in a lower cost per panel. This includes improvements in panel design, with more streamlined and durable panels being developed that require fewer resources overall. In addition, some companies have developed technologies that can produce solar panels more quickly and with fewer defects.
Factor #2: Increasing Production
As demand for solar power has grown, manufacturers have scaled up production, allowing them to take advantage of economies of scale. This has led to a reduction in the cost of materials, labor, and other expenses involved in producing solar panels. With the increasing demand for solar panels worldwide, manufacturers are building larger and more efficient factories, increasing their production capacity and reducing the cost of solar panels.
Factor #3: Innovative financing models
Leasing and power purchase agreements (PPAs) have made it easier and more affordable for individuals and businesses to adopt solar power. With these financing options, customers can install solar panels with little or no upfront costs and then pay for the electricity generated at a lower rate than they would pay for traditional grid electricity. This has made solar energy more accessible to a wider range of customers.
Factor #4: Government policies and incentives.
Government policies and incentives have also played a significant role in the expansion of solar energy. In many countries, government subsidies and tax credits have encouraged the adoption of solar power, creating a stable and supportive environment for the deployment of solar panels. Governments have also implemented policies that require utilities to use more renewable energy sources, which has helped to spur demand for solar power.
As a result of these factors, solar energy is now the fastest-growing source of new electricity generation worldwide. In 2021, solar PV accounted for nearly half of all new capacity installed globally, with the IEA reporting that solar power is now the cheapest source of electricity in history. According to a recent study, solar energy is expected to become even cheaper in the coming years, with costs projected to fall by as much as 60% by 2030.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rapid reduction in solar energy costs has been driven by a combination of technological advancements, increased production volume, innovative financing models, and government policies and incentives. With solar energy becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, it is clear that this renewable energy source will play an increasingly important role in the global transition to a low-carbon economy. As we move towards a more sustainable future, solar energy is likely to remain a key driver of progress.



